With the development of technologies, the amount of data is increasing exponentially. Traditional tools no longer cover the need to process and store information. To process data that exceeds hundreds of terabytes and is constantly growing, special algorithms have been created. They are commonly referred to as Big data.
Nowadays, huge volumes of information are collected from various sources: the Internet, IoT, mobile devices, etc. Most often, such data is unstructured, so a person cannot use it for any activity. To automate analysis, we use big data technologies. In this article, you will learn more about Big Data and its applications.
What is Big Data?
Big Data is a variety of large volumes of data stored on digital media. This includes general market statistics and personal user data: information on transactions and payments, purchases, movements, and audience preferences.
The volume of big data is measured in terabytes. It includes text, photos, and machine code. A human or an ordinary computer simply cannot analyze such an array of information; it requires special tools.
Also, whatever refers to Big Data can be defined through its application. From this point of view, Big Data is a collection of information that helps to make informed decisions. They make it possible to build predictive models of high accuracy.
Characteristics of Big Data
Big data is characterized by having "VVV" features:
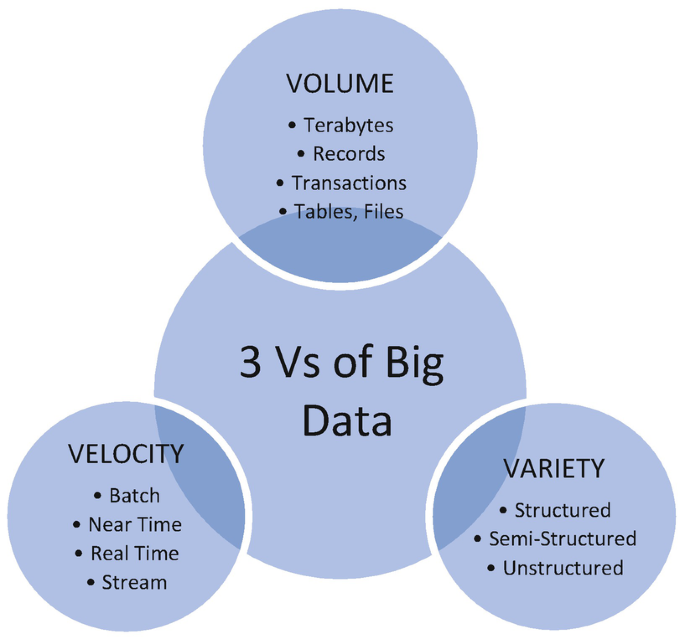
- Volume is the physical size of the data, its weight, and the amount of space it consumes. The flow of this data can be as much as 100GB per day.
- Velocity – information volume increases exponentially at a high speed and needs to be processed and analyzed quickly.
- Variety – data is heterogeneous and comes in different formats: text, pictures, voice messages, and transactions. They can be unstructured, fully or partially structured.
Additional aspects parameters
- Variability – the data flow is heterogeneous, with ups and downs. This makes it difficult to process and analyze.
- Value – describes both the complexity of the information and its degree of importance.
- Visualization – the possibility to visualize the results of an analysis to make it easier to perceive.
- Veracity – the accuracy and reliability of the data itself, as well as the correctness of the way in which the data is obtained.
How to Store Big Data?
Big data carries a lot of useful information that helps companies create new opportunities and generate business models.
Working with big data involves a number of steps:
- Data collection from different sources
- Management and storage
- Processing and analysis.
Stage 1. Data collection
At this stage, the company integrates technologies and systems that enable the collection of large data sets from a variety of sources.
Sources can be divided into three types:
-
Social is generated by people. Information uploaded or created by internet users: photos, emails, messages, articles, blog posts, etc.
-
Transactional refers to transactions such as purchases, money transfers, deliveries of goods, ATM transactions, link clicks, and search queries.
-
Machine learning - information from sensors and devices.
Stage 2. Management and storage.
The obtained data need to be stored somewhere, and this is a matter to be considered before working with the data. There are several options regarding data storage:
-
Local servers. The company procures, configures, and maintains the equipment.
-
Cloud server. The company leases cloud storage from a provider. Along with storage, some cloud platforms also provide ready-to-use solutions for data processing. This option is more expensive. On the other hand, the uptime, security, and support issues are handled by the provider.
These options are fine if there is not much data.
Big data is stored in data centers with high-performance servers. Often the data is distributed across multiple servers.
Distributing the data helps to process the information faster. This is possible because each piece of data is handled by a separate server, and the processing is done in parallel.
- Data Warehouse. This database was originally developed for business purposes, so it is well-structured and easy to understand and use. Data Warehouse is a repository of different data that has already been sorted and transformed. That is, the user has a collection of all necessary information that is stored in files or folders. This approach makes it easier and faster to use data for decision-making
- Data Lake is a repository where all raw data is stored in its original format without any conversion. Each item in Data Lake is marked with a unique identifier and a set of metadata tags. The data can be unstructured, semi-structured, or structured and is only converted when requested for use. Because of the complexity of the approach, Data Lake is more suitable for users engaged in deep data analysis and research.
Besides storage, Data Lake also includes software platforms, such as Hadoop, and defines sources and methods for data replenishment, clusters of storage and processing nodes, management, and learning tools. DataLake scales up to many hundreds of nodes when required without stopping the cluster.
Stage 3. Analysis
Big data is useful once it has been analyzed. This is the final stage of interacting with it. To do this, machine learning, association learning rules, genetic algorithms, and other technologies are used. After data analysis, only the most valuable data remains for the business.
The development of big data processing technologies offers great opportunities to improve the efficiency of various aspects of human activity: medicine, transport services, public administration, finance, and production. This is what has determined the rapid development of this technology in recent years.




