Cryptography refers to methods and techniques for encrypting information. It protects transmitted messages and uses algorithms proven in open environments to quickly detect and remedy any vulnerability.
Cryptography is an important layer of security in all aspects of digital business. It is the backbone of modern security systems. Cryptography secures transactions, protects sensitive data at rest and in motion, serves to establish trust between servers, and more.
This is why cryptography is a critical infrastructure, as more and more often, the security of sensitive data depends on cryptographic solutions.
Weak cryptography can expose critical infrastructure to vulnerabilities. Organizations should therefore pay attention to how cryptography is implemented and managed in the enterprise.
Types of Cryptography
Modern cryptography uses algorithms for encrypting and securely transferring data that cannot be cracked. The algorithms can only be processed by a computer and are based on mathematical transformations. Three cryptographic methods are most commonly used. Let's look at each one.
Symmetric cryptography
One of the oldest and simplest ways of encrypting. Symmetric cryptography uses a secret key, either a number, a word or some random characters, to encrypt and decrypt data. Both sender and receiver know these keys. This method is not normally used for internet communications, as the key must be transmitted separately. If a third party somehow obtains the key, they will be able to view the encrypted data. Thus, symmetric cryptography is suitable only for encrypting local databases, e.g. on a server hard disk.
Pros:
- The only cipher with absolute theoretical persistence - all decryption attempts are worthless.
Cons:
-
Impossibility to identify the responsible party in the event of a leak.
-
Requires an open channel for transmitting the secret key.
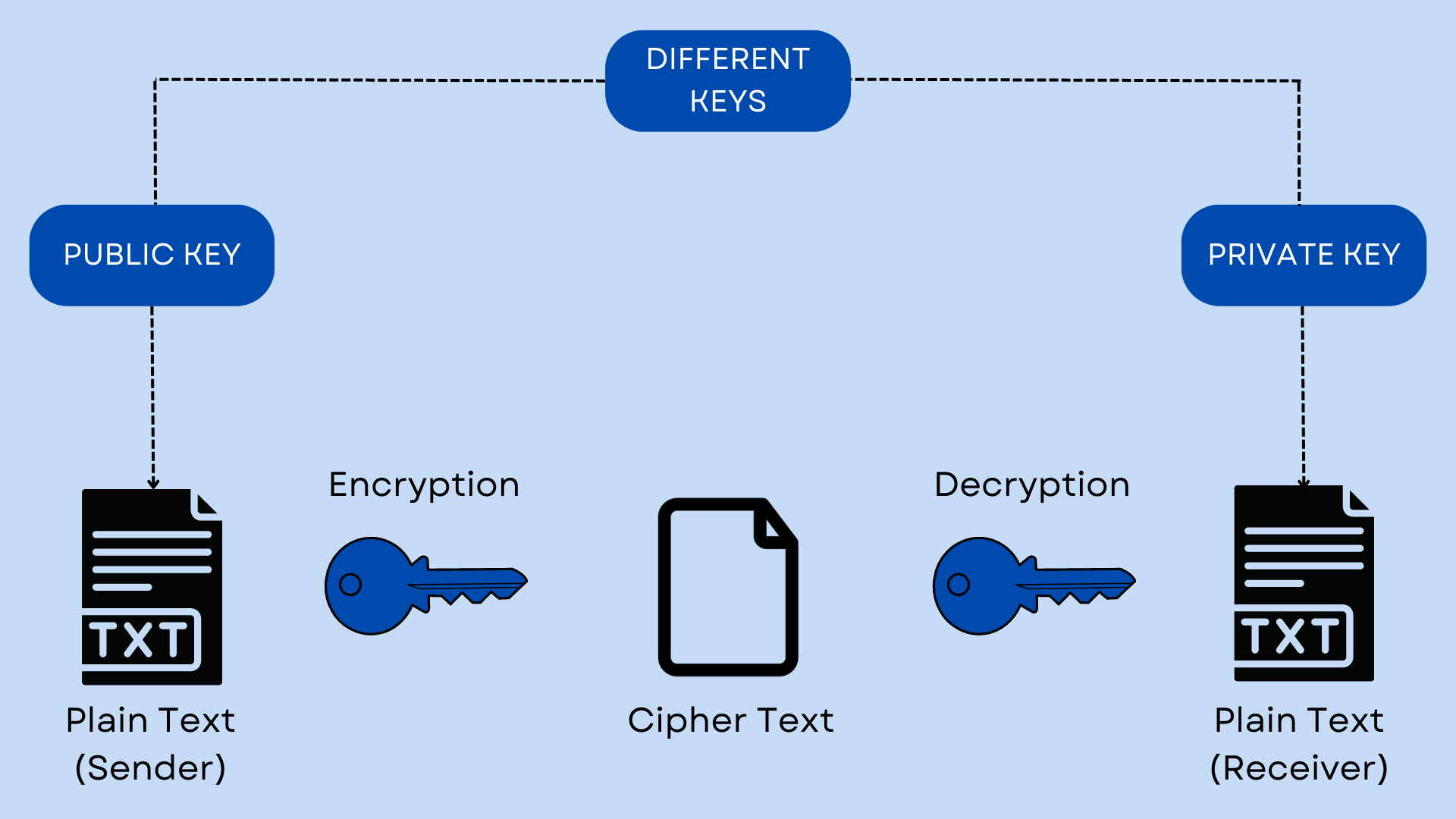
Asymmetric encryption
An encryption method involves the use of two keys, a public key – to encrypt information, and a private key – to decrypt data. The public and private keys are very large numbers linked by a specific function, but in such a way that if you know one key it is extremely difficult to calculate the other. Keys are very large numbers linked by a certain function, but in such a way that if you know one key, it is extremely difficult to calculate the other.
Pros:
-
No need to create a secure channel for the transmission of the secret key – all interactions take place in an open channel;
-
Having a single copy of the key reduces the chances of its loss and allows for personal responsibility for maintaining secrecy;
-
Having two keys enables two forms of encryption - secret communication and signature.
Hashing
This method does not encrypt data but converts information into a unique set of characters. Hashing is not intended to hide messages but rather to verify their content.
Hashing is a useful method of checking downloaded files, for example, if you need to update the software on a computer. Once you download an update, you get a hash of the file along with it. The computer hashes the downloaded file again and compares the hashes: if they match, it means that the file is undamaged. Even the slightest change to the downloaded file, caused by corruption or intentional tampering, will drastically change the resulting hash. Only after the integrity check can the computer continue to work with the file.
Pros:
-
It is impossible to calculate the source data from the hash or to retrieve other data with the same hash for a cryptographic hash function;
-
Using the key value, data can be decrypted in a single operation;
-
The hash can be transmitted after the calculation and stored separately from the data. It can be recalculated.
Cons:
-
You cannot reverse hash and recover the original data;
-
If the hash function is not crypto-resistant, it can be hacked by brute force.
What is cryptography used for?
In today's world, cryptography is used everywhere. For example, for secure sending passwords over networks when shopping online. Bank servers and email clients store user passwords using encryption methods.
Security professionals use cryptographic techniques to maintain data secrecy, authenticate the identity of senders and recipients, ensure the integrity of data by providing evidence that it has not been tampered with, etc.
Banking transactions would stop, internet traffic would cease and mobile phones would stop working without cryptography. All of our sensitive information would be available to the public, causing damage if it fell into the hands of malicious parties.
Cryptography prevents such threats by securing information with rules that allow only authorized people to receive and process data.




