In our digital age, data is the cornerstone of organizational value. Businesses generate and store vast quantities of information every day, making data security more important than ever. Cyber threats, hardware malfunctions, natural disasters and human mistakes can lead to catastrophic data loss, jeopardizing a company's operational integrity and reputation. In the article, we observe the transformation of data protection strategies, and one solution that has gained prominence – Backup-as-a-Service (BaaS).
What is cloud backup?
Cloud backup involves storing data on remote servers accessible via the Internet, rather than relying solely on traditional on-site storage solutions that require extensive hardware and infrastructure. This approach allows organizations to back up their data off-site, protecting it from local disasters such as fires or floods.
One of the outstanding features of cloud backup is its flexibility. Businesses can easily scale up or down their storage requirements as their needs change, without having to purchase additional physical equipment. For example, a startup can launch with a small storage plan and expand as it grows, paying only for the capacity it actually uses.
Defining Backup-as-a-Service (BaaS)
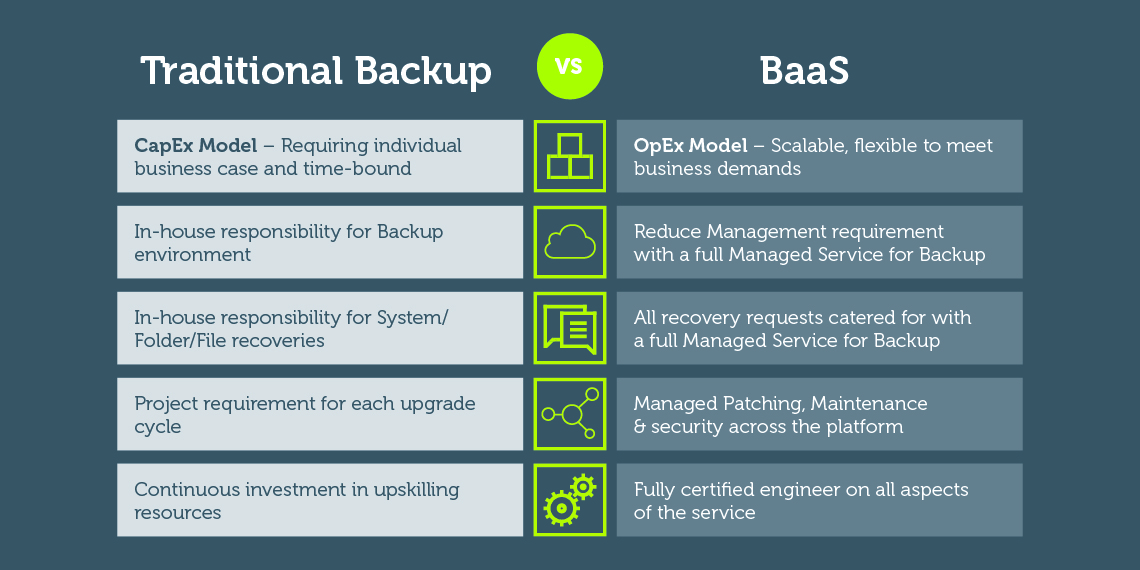
BaaS elevates the concept of cloud backup by offering a holistic solution managed by third party providers. The service includes not only data storage, but also automated backups, recovery solutions and continuous monitoring.
Consider a fast-growing online retailer facing a peak in activity during the busy sales season. Manually managing backups can quickly become overwhelming as the volume of transactions and customer data increases. By using Backup-as-a-Service, the retailer can automate processes, ensuring that critical information is protected without taking focus away from core business operations.
Benefits of Backup-as-a-Service
1. Cost Efficiency: When considering which option to choose - cloud or on-site backup - keep in mind that traditional backup solutions often have high upfront costs for hardware and software. In contrast, with the cloud, organizations pay only for what they use. This reduces capital expenditures and turn them into manageable operational costs.
2. Improved security: In today's environment of cyber threats, robust data security is critical. Providers employ advanced security protocols, including encryption and strict access controls.
3. Disaster recovery capabilities: A reliable backup solution can be vital when the unexpected happens. Many BaaS providers include disaster recovery options that can help recover systems quickly. For example, if an organization falls victim to a ransomware attack, it can revert to its last clean backup, significantly reducing downtime and financial loss.
4. Convenient accessibility: Cloud-based solutions allow users to access their data from virtually anywhere – a significant advantage in today's remote and hybrid working environments. Employees can work with necessary files without having to be physically present in the office.
5. Regulatory compliance: Various industries are subject to strict data protection and privacy regulations. When choosing a cloud backup provider, consider whether they have built-in compliance measures in place to meet regulatory requirements.
Potential challenges
Despite the many benefits of BaaS, organizations should be aware of potential challenges. One concern is vendor lock-in; moving between providers can be complex if data is stored in proprietary formats. It is important to choose providers that support open standards and facilitate easy data migration.
Another challenge is bandwidth constraints. Large-scale backups can consume network resources, potentially impacting day-to-day operations. Organizations should evaluate their network capabilities and consider scheduling backups during off-peak hours to mitigate this issue.
Transition steps
Implementing Backup-as-a-Service requires careful planning and execution. Here are some steps to take:
-
Assess data requirements: Determine what data needs to be backed up and how often.
-
Select the right provider: Research different providers based on features, pricing models, security protocols and customer support. Look for testimonials and case studies to assess their reliability.
-
Develop a backup strategy: Create a comprehensive backup strategy that includes scheduling, retention policies and disaster recovery plans.
-
Run regular tests: Test backups regularly to ensure that data can be recovered quickly and accurately when needed.
-
Educate employees: Train staff on the importance of data protection and how to effectively use the chosen backup solution.