Virtualisation is a set of technologies for the software separation of physical computing system resources and applications into isolated virtual machines (VMs). Each VM runs on a dedicated portion of the resources as a completely independent hardware platform.
Virtualisation is rapidly changing the IT landscape. There are many reasons why organisations are embracing this technology. The most important is to reduce IT costs while getting the most out of hardware. In addition, a virtual infrastructure provides greater flexibility and scalability, enables easier workload management, and increases productivity and resource availability. In this article, we will take a closer look at virtualisation technology and the types and products available.
How Does Virtualization Technology Work?
The architecture of a virtual server is more complex than that of a traditional physical server. The most important part of the system is the hypervisor. It provides an abstraction layer between the software and the actual hardware. With the hypervisor installed, the software relies on virtual representations of computing resources, such as virtual CPUs instead of physical CPUs.
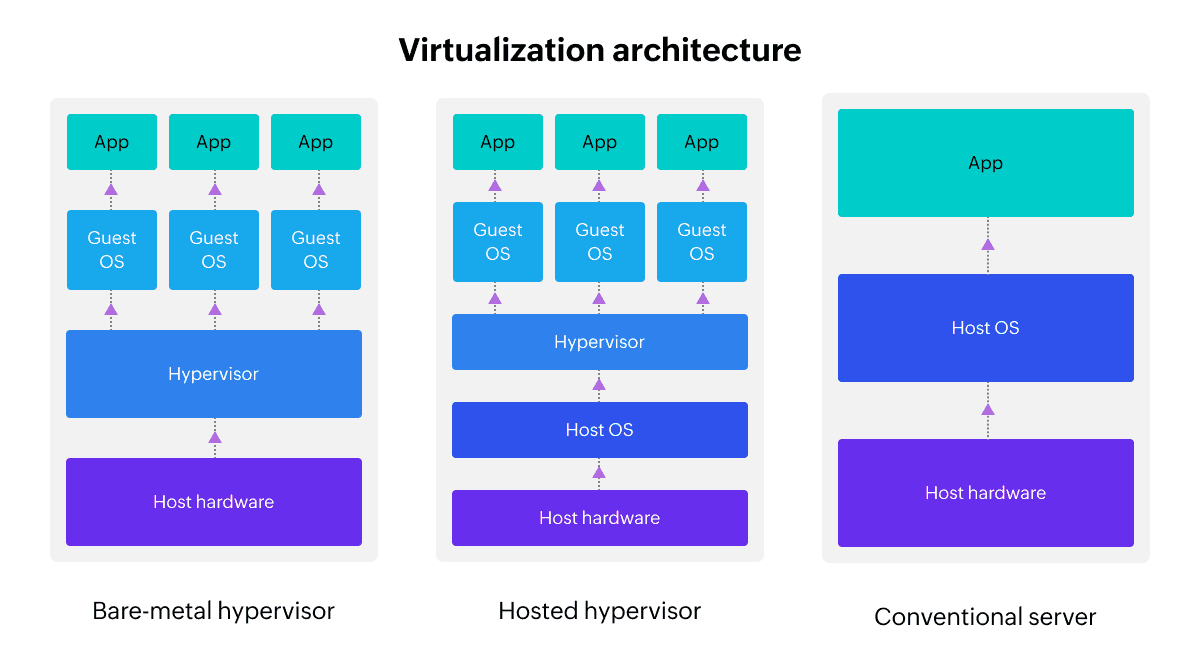
The pooled virtualised computing resources are called virtual machines. You can install the operating system and required applications on the VMs. Virtualised systems contain multiple virtual machines running simultaneously, each logically isolated from the others. If one of the VMs is overloaded or hacked, the other machines in the system are not affected.
Because the hypervisor is installed directly on the server and operating systems, this approach is often referred to as bare-metal virtualisation. Another option is to install the host operating system first and then deploy the hypervisor and all the VMs within it. This method is often referred to as host system virtualisation and is most commonly used for container virtualisation.
Types of Virtualization
Server virtualisation. This technology allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical machine, each simulating the operation of a separate server. The software simulation affects the main components of the server: processor, memory, RAM and others. Server virtualisation is essential in a production environment because it reduces the need for hardware resources and delegates their functions to virtual machines. This approach saves on hardware purchases and upgrades, and reduces power consumption.
VMware vSphere is the industry's leading virtualisation platform for building cloud infrastructures. It provides stability for business-critical applications and the ability to respond more quickly to changing business needs..
Storage virtualization is a way of representing storage resources as logical storage spaces (volumes) without tying them to physical storage devices. The technology provides a convenient and transparent way to manage storage when real storage devices connected by different protocols are perceived as a single pool. Storage virtualisation improves performance, resiliency, availability and security. It optimises storage utilisation, simplifies both migration and mirroring, saves on IT expansion and allows you to organise tiered storage.
VMware Virtual SAN is an enterprise-class storage solution for hyper-converged infrastructure optimised to work with today's flash-based systems. VMware Virtual SAN (vSAN) provides space for virtual disks that contain the data needed to run virtual machines.
Application virtualization. With this approach, applications are not installed in the operating system, but can simply run on the selected machine. The components of the operating system required by the application are emulated. Each application is given its own isolated environment to run independently of other software..
Workstation virtualization. Known as VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure), this technology is widely used in the workplace and brings many benefits to businesses. The virtual desktop resides on the cloud provider's servers, not on the user's computer. All of the user's data and applications are hosted on the remote servers, giving the user many options, including access from different devices and locations.
VMware Horizon is a state-of-the-art platform for securely delivering virtual desktops and applications in the hybrid cloud. The solution helps IT departments efficiently deploy and scale virtual desktops and applications. With rapid provisioning, automation, and simplified management, it delivers the most comfortable digital workspace experience to end-users.
Network virtualization. In this case, the virtualisation software fully emulates the operation of the physical data network components. You can perform the same actions on a virtual network as on a physical network. This increases efficiency and allows you to work independently of the hardware. For example, workloads can connect to any emulated network device such as switches, logical ports, routers, VPN networks..
VMware NSX is a network virtualisation and security platform for software-defined datacenters that enables entire networks to be created and run in parallel on existing network hardware.
VMWare software is one of the most popular and widely used virtualisation tools today, and its hypervisor is the leader among similar solutions from other vendors..
Cloud4U supports a wide range of VMware products and services. You can migrate all workloads from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud or create a hybrid cloud environment that can be managed from a single location.




