Every day we use cloud services not even aware of that. All kinds of storage, streaming services, social networks, and portals are all powered by cloud solutions.
Cloud technologies are attractive because of their cost-effectiveness, performance, reliability, and scalability. Migration to a cloud platform addresses several issues related to resource capacity, compliance with legal requirements, and employee mobility.
Cloud infrastructure consists of hardware and software elements. The main physical components are networking equipment, servers, and storage. It also includes a hardware abstraction layer – a hypervisor, which enables virtualization
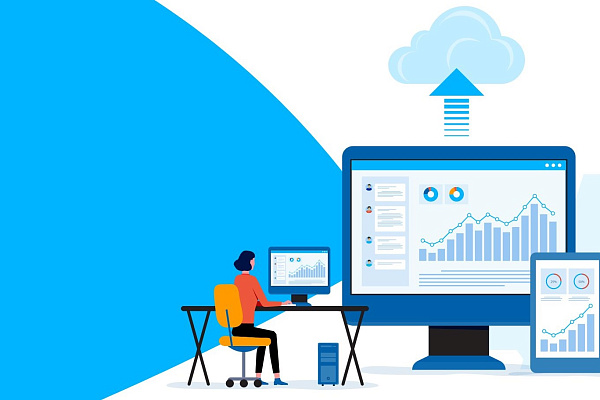
There are three types of cloud deployment models: private, public, and hybrid clouds. In this article, we will observe, how each type of cloud differs from the other, and which one is suitable in different business scenarios.
Public cloud
This is the most common form of cloud deployment model, in which the provider provides access to resources over the Internet. In this case, you do not have to worry about the cost of hardware or keeping it up to date.
With built-in tools, public cloud infrastructure is easy to manage, even non-IT professionals can cope with this task. You can create additional virtual machines, delete the existing ones, configure isolated and routed networks, and more.
Public does not mean shared data. Virtual machines from different customers are isolated from each other. Public cloud implies that your data may be physically stored on the same physical server as other companies' data, but they do not have access to it.
One can never say for sure, which physical hardware your virtual machines will be, because when stored in a cluster, virtual machines are moved between servers for load balancing and better fault tolerance. What makes the cloud public is the allocation of resources from a common public pool, but user data is protected.
Since cloud providers can guarantee your uptime across the globe, public cloud is popular among geographically distributed companies. Also, with the pay-as-you-go billing model, the public cloud responds well to unpredictable usage and scalability.
Private cloud
This is a model when the cloud environment is dedicated to one tenant. It does not matter where the infrastructure is physically located. It is called private if the equipment is located on company premises or in a third-party data center. Cloud providers offer such a solution. For example, Cloud4U has a Private Cloud 2.0 solution.
The advantages of the solution:
- high level of security;
- full isolation of infrastructure;
- hardware control;
- enterprise-class hardware (HP blade servers, NetApp storage systems);
- rapid resource scaling;
- 24x7 support.
Hybrid cloud
This is a combination of private and third-party public cloud environments. Hybrid cloud allows deploying workloads in both environments and moving between them. When your capacity is insufficient, you can use the external one. For example, if on-premises storage transfers a large amount of data to the public cloud for processing. Hybrid clouds enable you to increase capacities in case of peak loads.
To summarize, each of these models is cloud-based.
All the dedicated computing power is accessible via the Internet from any device. However, in a private cloud, you get the equipment that belongs only to you, and in a public one, the resources are virtual.
Differences between the private cloud, hybrid cloud, and public cloud models
You might think that all three types differ only in architecture, being almost identical in other parameters. However, that is not correct. Here are several variables to consider when making a choice.
Elasticity and scalability. In terms of the potential to quickly allocate the capacity you need, the public cloud outperforms the private one, as you can have almost unlimited resources. If scalability of resources is important to you, choose the public cloud.
Services availability and continuity. In a public cloud, even in the event of a failure, data will not be lost. In a private cloud, you need to set up backups and organize the distribution of data across 2-3 data centers. It is complicated and expensive. Cloud providers have all the hardware and software solutions to protect data and maintain the customer's service sustainability. This is included in the service price. There are also additional features: load balancers, business continuity and disaster recovery services. They can be easily connected via the control panel. If data loss or service unavailability is critical for you, but you do not want to pay too much, choose a public cloud.
Software and hardware. Public cloud providers offer customers up-to-date hardware and software. Latest technologies that make the infrastructure more user-friendly or increase its performance – this is what the cloud provider focuses on. With a private cloud infrastructure, this will be the responsibility of the customer.
All of the above-mentioned does not mean public clouds have no drawbacks. They create a dependency on an Internet connection, which must be stable and fast to use cloud resources at any time. Besides, virtualization slightly affects the configuration of resources. And, of course, it is necessary to pay a monthly fee for the consumed resources.
Hybrid solutions are convenient because they allow you to leverage the benefits of both types of cloud platforms, distributing data across different cloud environments and reducing the virtual infrastructure costs. However, there is another challenge: You have to "match" everything correctly and without compromising security.
Cloud Deployment Models – which one to choose
Clouds are convenient. But how much will it cost a company? The answer to this question depends on how you deploy your infrastructure.
You can deploy a private cloud in two ways.
Building on your own facilities, and then maintaining it yourself
Renting part of the data center and equipment from a provider. This involves expenses on the equipment and preparing a cloud platform. You can choose open source solutions, but then you need experts skilled to work with this platform and be able to modify it to meet your needs.
A public cloud is easier to deploy. All you need to do is select the necessary service in the administration panel, and then you can migrate applications and data to it. This work can be handled by the in-house IT department or the provider's specialists.
The cost of hybrid solutions is determined by the cost of private infrastructure and resources rented from the public cloud.
Cloud4U cloud solutions
Our platform allows you to create private, hybrid, and public clouds. We draw your attention to the Private Cloud 2.0 solution, which gives you the right level of security and performance at a reasonable cost. It is a cloud model that combines hybrid and private models.
If you have any concerns regarding the choice of solution and selecting a pool of resources, our managers are ready to help and answer your questions. Migration challenges or any other technical issues can be solved with the help of Cloud4U technical support. Call +44 20 80 89 80 01 or use online chat on our website.




