An IP address is the numerical identifier of a device connected to a network. Every PC, laptop, camera, etc., connected to the Internet has a specific IP address. To be more precise, IP is a set of four digits from zero to 255 separated by a dot, e.g. 192.168.243.12. There are different IPs: external and internal, static and dynamic, public and private. In this article, we will discuss the latter.
What is public IP
All devices directly connected to the network have a public IP address. If you know this address, you can directly contact the specific device. On a simple, small network, this is easy. However, with the Internet, this scheme no longer works. Four bytes can give about 4.3 billion unique IP addresses. In the early days of the Internet, this number seemed to be far more than enough. Nowadays there are more than 20 billion network devices. There are simply not enough white IP addresses for everyone.
The sixth version of the IP protocol solves the problem. Its address consists of 16 bytes, which gives 3.4 ∙ 1038 unique combinations. It is the public address used on the Internet. Public IPs are routed on the Internet, unlike private addresses.
Having a public IP address on your router or computer will allow you to organize a server (VPN, FTP, WEB) or remote access to PC and CCTV cameras, and get access to them from anywhere.
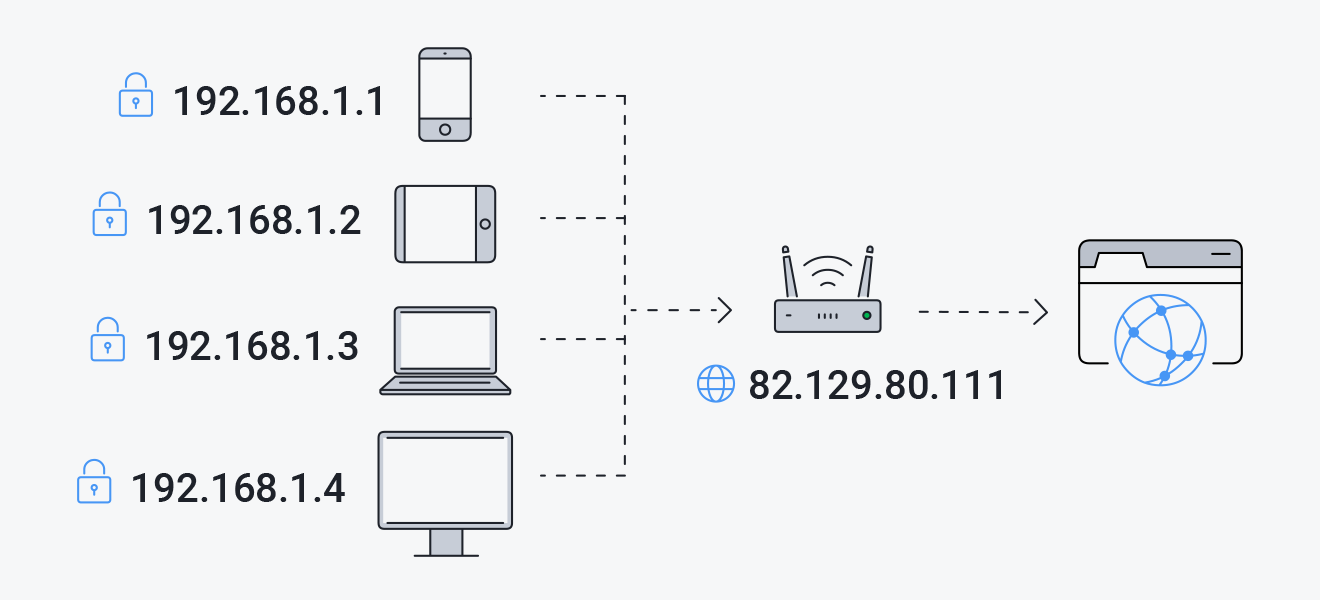
For home users, the ISP may provide only one or several public IP addresses. The router allows devices on the home network to use a single public IP address, installed on the WAN interface of the device through which it connects to the Internet. This external public IP address can be used to access your home network PC from the Internet, but to do so you need to use port forwarding on the router
Since the number of white IP addresses is limited and the number of Internet users is growing, ISPs tend to use private (grey) IP addresses assigned to users.
Public IP ranges
-
1.0.0.0 - 9.255.255.255
-
11.0.0.0 - 126.255.255.255
-
129.0.0.0 - 169.253.255.255
-
169.255.0.0 - 172.15.255.255
-
172.32.0.0 - 191.0.1.255
-
192.0.3.0 - 192.88.98.255
-
192.88.100.0 - 192.167.255.255
-
192.169.0.0 - 198.17.255.255
-
198.20.0.0 - 223.255.255.255
What is private IP
A private, or grey address, is the IP address of a device on a local network that is not directly connected to the Internet. Such addresses are unique only within the network itself. With their help, devices within the local network communicate freely with each other. It is not possible to establish a direct connection with devices on another network.
Grey IP addresses belong to ranges reserved for local networks and therefore not used on the Internet. These ranges include:
-
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255
-
100.64.0.0 - 100.127.255.255
-
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255
-
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255
A computer with a grey IP address can access the Internet using hardware or software routers.
To the rest of the Internet, the owners of grey IP addresses are visible to the white IP address of the router. In particular, customers of the same ISP receiving grey addresses are visible to the rest of the Internet under the same IP address.
Public vs. Private IP
Public and private addresses have different purposes, so it would be incorrect to discuss which one is better. However, let's try to highlight the advantages and disadvantages:
Using local IP allows you to spend less of public addresses. They are limited, as there are a huge number of devices in the world, and it is impossible to set a unique number for each one.
Local IPs provide an additional layer of security. Since they are not routed directly through the Internet and are not accessible from outside the local network, it creates a barrier to protect internal devices from intrusions. Organizations can use network mechanisms such as Network Address Translation (NAT) to convert local IPs to public IPs when connecting to an external network.
The disadvantages include:
-
If IP is blocked, all local IPs hidden behind a public address will be blocked as well.
-
The more local addresses working through the public address, the lower the connection speed.
How to determine the IP address
You can use the following simple methods:
-
Third-party service. There are special sites that offer this kind of service. They show only white addresses.
-
By command in the terminal. This method allows you to find both public and local IPs.
For Windows, press Win + R and then type cmd at the prompt and press Enter. Next, type ipconfig.
For Linux, press Ctrl + Alt + T. Next, type ip a




