Sometimes even experienced users think that virtual servers and the cloud are the same thing. However, there are several differences between VPS, VDS, and the cloud. In this article, we will explore these three popular ways of hosting and find out which one is better in different business scenarios.
Both options – Virtual Private Server and Virtual Dedicated Server – involve providing the client with virtual servers with defined parameters. Sometimes they differ in terms of virtualization technology. VDS is typically based on hardware virtualization, while VPS means virtualization at the OS level.
What is a VDS Virtual Server?
A Virtual Dedicated Server (VDS) is a type of hosting service that provides a dedicated virtual server environment. That is your isolated server environment with dedicated resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage.
With VDS, businesses have full root access to their server. They can install software or configure the server environment as they wish. This technology is essential for companies that require control over their hosting environment as well as a high level of security.
As requirements increase, VDS is easy to scale by adding resources. This ensures that businesses can deal with increased traffic without affecting performance.
What is a VPS virtual server?
Virtual Private Server (VPS) just like VDS provides businesses with a virtual server environment. However, there are a few key differences.
With a VPS, multiple websites also share the same physical server, and while resources are still shared, each site gets its resources. This ensures better performance. For example, if one site experiences a sudden spike in traffic, it will not affect other sites on the same server.
In addition, VPS provides enhanced security through the isolation. This means that if one site is hacked, it will not affect the security of other ones on the same server.
What Is a Cloud Server?
A cloud server is a virtual machine that runs on the physical resources of a provider. Users access a server via the Internet. The main advantage of a cloud server is scalability – you can increase the amount of resources as needed in a few clicks, without worrying about investing in additional hardware. This makes it easy to adapt to changing business requirements.
Also, cloud servers are hosted in multiple geographically dispersed data centers, meaning that if one server fails, resources can be quickly and seamlessly migrated to another data center. Customers get access to its resources from anywhere, enabling them to work remotely or collaborate with employees from different locations.
Providers typically employ robust security measures to protect clients’ data and server resources, which ensures enhanced security of the cloud.
VPS/VDS vs. Cloud
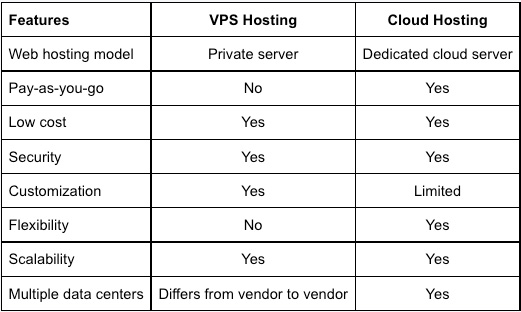
With cloud servers, businesses do not have access to a dedicated server environment. Instead, they share resources with other businesses hosted in the cloud. This is the main difference. However, this is not a problem, as cloud hosting providers use advanced resource allocation technologies to ensure every business has access to the resources it needs.
While the cloud differs from VPS/VDS in terms of the level of dedicated resources provided, it is an excellent option for businesses looking for a scalable and reliable hosting solution. Cloud servers often come with a range of additional services, such as automated backups, load balancing, and content delivery networks (CDNs). These features help optimize website or application performance and improve overall user experience.
In general cloud servers offer businesses a cost-effective and flexible hosting solution that can help them stay competitive in today's fast-paced digital landscape. Companies can focus on what they do best: growing their business and serving customers.
Cloud vs. VPS/VDS hosting: Which to choose?
Each option has its pros and cons, but how to choose the best one? In many respects, the choice depends on your tasks and finances.
If the budget is limited, use VPS hosting. It is cheaper than purchasing physical equipment, and compared to clouds, the cost is lower. Keep in mind, however, that you will need specialists to set up the infrastructure, and this is an additional investment. VPS is difficult to scale, and fault tolerance is much lower than in the cloud. This solution is well-suited for hosting websites.
Thecost of cloud services is higher, but you can flexibly choose the configuration
for your needs, scale in one click, and pay only for the consumed resources.
Cloud infrastructure is the best option for large projects, as well as for
companies with fluctuating capacity consumption.




