In today’s fast-paced digital economy, businesses demand IT infrastructure that is both resilient and adaptable. Virtual servers have emerged as a foundational technology enabling this agility. Let's explore what virtual servers are, how they support modern cloud environments and discover why they are essential for businesses.
What is a virtual server?
A virtual server is a software copy of a physical server created using virtualization technology. Organizations achieve unprecedented resource efficiency by dividing a single physical server into multiple isolated virtual machines (VMs), each with its own operating system and applications.
The magic lies in the hypervisor. This is a software layer (such as VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V) that allocates CPU, memory and storage to VMs, allowing them to operate independently.
How virtual servers power the cloud
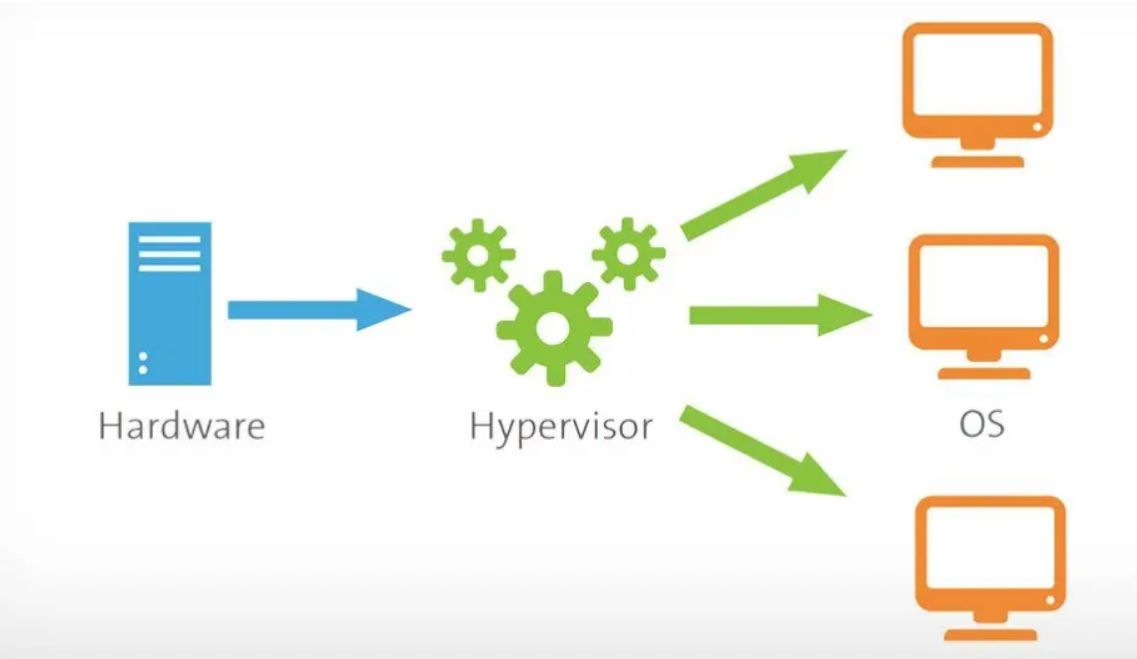
Virtual servers are the core of the cloud infrastructure, enabling three key functions:
-
Resource optimization: A single physical server can host dozens of VMs, reducing hardware costs and energy consumption. For example, an IBM study found that server consolidation through virtualization could reduce energy costs by up to 80%.
-
Multi-tenancy: Cloud providers use server virtualization to deliver services to multiple customers on shared hardware.
-
Elastic scalability: Spin up or spin down VMs in minutes to match resources to demand - a critical advantage in changing business markets.
Why virtualize servers?
Virtualization is transforming IT infrastructure by increasing efficiency, resilience and scalability – all while streamlining operations.
Space efficiency
Replace bulky, under-utilized physical servers with multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single host. Reduce hardware costs and data center sprawl.
Fail-safe operations
If one VM crashes, others on the same host continue to run. This built-in redundancy eliminates downtime for critical systems.
Zero downtime
If hardware fails, VMs automatically restart on healthy servers. Mission-critical apps stay available 24/7.
Key benefits for businesses
1. Cost Efficiency and Consolidation
Virtualization reduces capital expenditure by eliminating the need for physical servers. According to Gartner, organizations that virtualize 75% of their servers can save 40% on hardware costs. A Dell Technologies case study found that a financial services company reduced its server count from 500 to 50 through virtualization, saving $2 million annually.
2. Agility and rapid deployment
Virtual servers allow companies to deploy applications in minutes instead of weeks. For example, Netflix uses AWS EC2 instances (a form of virtual server) to scale its streaming infrastructure during peak demand, ensuring a seamless user experience.
3. Disaster recovery and high availability
4. Test and development efficiency
Addressing limitations
While virtual infrastructure offers value, there are challenges:
Resource overhead: Hypervisors consume 5–15% of system resources, requiring careful capacity planning.
Security: Vulnerabilities such as hypervisor exploits are rare but critical. In the cloud, this is mitigated by micro-segmentation (e.g. VMware NSX) and regular audits.
Choosing the right cloud provider
When selecting a virtual server provider, consider the following key priorities:
SLA commitments: Ensure uptime guarantees (e.g., 99.99%) and disaster recovery protocols.
Hardware quality: Look for NVMe storage and scalable CPU architectures.
Data center reliability: Certifications such as ISO 27001 and Tier III compliance indicate a robust infrastructure.
Conclusion
Virtual servers are not just a cost-saving tool — they empower businesses to innovate faster, scale smarter, and compete in an era where IT agility defines success. Whether you’re migrating legacy systems or building cloud-native apps, virtual servers are the key to unlocking your infrastructure’s full potential.