As remote and hybrid working formats emerge, companies need to provide employees with a secure work environment. Key technologies that support this format include Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), Remote Desktop Service (RDS) and Desktop as a Service (DaaS). In the article, we will compare and contrast these desktop virtualization solutions.
What is VDI?
VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) is a form of desktop virtualization that delivers remote workstations from a centralized server using a client-server model. This allows all users to access the same administrator-managed software, ensuring consistency across the organization.
In essence, VDI combines hardware, software, and networking to distribute virtual desktops to end users, who can access them from any network-connected device. Each virtual machine (VM) is allocated dedicated resources for improved efficiency and security, with multiple VMs running on a single physical server or a clustered virtual server.
VDI supports two types of desktops:
-
Persistent: Customizable for individual users, retaining personal settings, applications, and data. Users with admin rights can even install their own software.
-
Non-persistent: Assigns users a generic desktop from a pool, resetting after each session for a clean slate.
Primarily used in large corporate environments, VDI enables employees to log in from any device while maintaining a consistent desktop experience. This flexibility boosts productivity but comes with challenges — VDI is complex to deploy and maintain, requiring skilled IT personnel. Additionally, high overhead costs arise from additional hardware, multi-device licensing, and Windows OS fees per user.
VDI use cases & benefits
-
High-security industries (finance, healthcare, government) needing strict compliance.
-
Large enterprises requiring full control over infrastructure.
-
Remote teams needing a consistent desktop experience across devices.
What is RDS
Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is a multi-user virtualization platform that enables multiple employees to simultaneously access a shared environment. Unlike VDI, RDS operates through session-based virtualization. This means that teams collaborate on the same OS instance while running applications remotely.
How RDS works
- Leverages Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) for secure connections.
- Hosts multiple user sessions on a single Windows Server OS.
- Delivers published applications or full desktop experiences.
- Optimizes resource usage by sharing CPU, memory, and storage across users.
Advantages of RDS
-
Cost-efficiency – Eliminates the need for individual VM allocations.
-
Streamlined IT administration – Manage one OS image instead of hundreds of desktops.
-
Flexible deployment – Choose between on-premises servers or cloud-hosted RDS.
What is DaaS
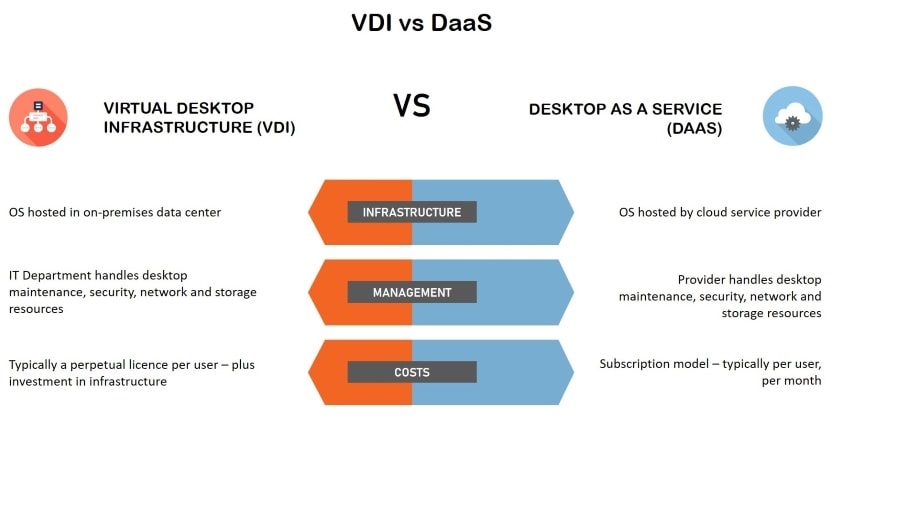
DaaS (Desktop as a Service) represents the next evolution of VDI, where organizations rent cloud-hosted virtual desktops instead of maintaining physical infrastructure. Providers handle all backend management while businesses enjoy enterprise-grade virtual workstations on demand.
DaaS Deployment Options:
- Persistent Cloud Desktops
- Maintain user customization between sessions
- Perfect for designers, developers, and power users
- Stores profiles in cloud storage
- Non-Persistent DaaS Environments
- Resets to a clean state after logout
- Ideal for shift workers, call centers, and temporary staff
- Reduces storage costs through shared images
Final Thoughts
The decision between VDI, RDS, and DaaS requires careful consideration of your organization's technical requirements, budget, and long-term strategy. Each solution offers unique advantages that align with different business scenarios:
VDI remains the gold standard for enterprises in highly regulated industries like finance, healthcare, and government, where data sovereignty and strict compliance are non-negotiable.
RDS is perfect for SMBs that prioritize cost efficiency and operational simplicity. Its session-based architecture makes it ideal for task workers who primarily need access to standardized applications without full desktop personalization.
DaaS is transforming how agile enterprises and distributed teams operate by eliminating infrastructure management and enabling instant, global scalability. With predictable pricing and automatic updates, DaaS is particularly compelling for businesses embracing hybrid work.
To make a choice follow these steps:
-
Assess user workflows (Do teams need full desktops or just apps? Are workloads static or variable?).
-
Audit security/compliance mandates.
-
Compare TCO over 3–5 years (factoring in IT labor, scalability needs, and refresh cycles).
Need expert guidance? Cloud4U’s specialists can help you design, deploy, and optimize the right solution for organizing remote work. Contact us today for
a tailored assessment.