In the digital age where mobility and flexibility have become essential requirements for work and education, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) is not only a trend but also a necessity. VDI is an innovative IT solution that allows users to connect remotely to the desktop. Not only is this convenient, but it also improves business productivity by providing access to your personal workspace from any device and anywhere in the world.
VDI Technology
VDI is a system for virtualizing desktops. Unlike traditional PCs, all the data that employees interact with is stored on a central server, and each employee has access to it via a virtual desktop. There is nothing on local media; no external media can be connected.
This allows you to reduce the load on end-user devices such as PCs and thin clients, turning them into portals rather than standalone machines.
How VDI works
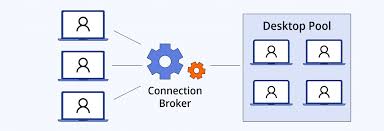
VDI works on the client-server principle. Each user connects to the desktop over the Internet or a local network. When users log in, they have access to a virtual desktop that is an exact copy of the operating system interface. This copy resides on a central server and is streamed in real time.
This provides a seamless experience as if the OS was running directly on the user's computer. This makes the working environment mobile and accessible, which is particularly important in today's flexible working environment.
The pros and cons of virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI)
Let's list the pros:
-
Centralized management. All desktops can be managed from one place, simplifying updates and security.
-
Anywhere access. Users can access their desktop from any device, anytime.
-
Resource savings. Reduce hardware costs as thin clients cost less than full PCs.
-
Security. Data is not stored on local devices, preventing it from being lost or stolen.
-
Scalability. Changes in the number of jobs and resources can be made quickly and easily.
-
Energy efficiency. Thin clients use less power than standard computers.
Of course, there are also cons:
-
Network dependency. Highly dependent on the quality and speed of the Internet connection.
-
Upfront investment. Initial investment in server hardware and licences can be significant.
-
Complexity of installation. Qualified IT professionals may be required to install and manage VDI.
-
Performance. The performance of a virtual desktop can be less than that of a local computer, especially for resource-intensive tasks.
-
Compatibility issues. Some applications and devices may be incompatible with virtual desktops.
VDI benefits
VDI offers significant benefits to business and education. It promotes mobility, security and centralized management.
Despite some drawbacks, such as network dependency and start-up costs, the technology is evolving to provide more efficient and integrated solutions for the modern working environment.
For organizations looking for scalability and versatility in their IT structure, VDI can be an important technology to help them keep up with the times. With the increasing shift to digital and remote working, investing in VDI is an important step in meeting the needs of today and tomorrow.
How to implement VDI
We have learned what VDI is and how virtual desktops benefit your business. Now let's look at how the technology can be implemented.
The system consists of the following components:
-
High-performance servers either leased from a cloud provider or your own servers installed in a data center under a colocation agreement.
-
Virtualization platform from Microsoft or VMware, VDI/TS (Terminal Server) software.
-
MS Hyper-V or Active Directory licenses.
-
Thin clients may not be purchased separately if your PCs meet operational requirements.
Check the bandwidth of the local network to see if it can support data transfer at the required speed. Two parameters are important - normal and peak network load, which determines the stability of the infrastructure. Also, consider the login, response and server load time when all the virtual PCs are switched on at the same time.



