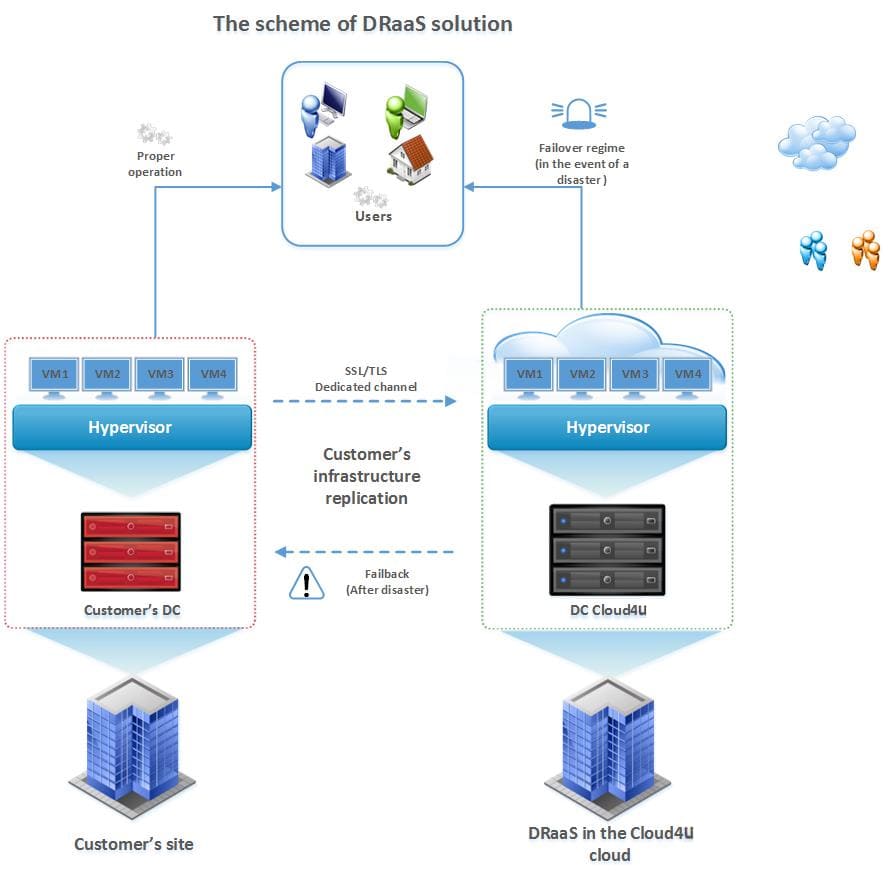
Disaster Recovery (DRaaS)
Disaster Recovery-as-a-service (DRaaS) is a cloud service that ensures fast recovery of workflows and services in the event of a disaster or force majeure in the main data center.
Disaster recovery for business continuity needs
Disaster Recovery Service (DRaaS - Disaster-recovery-as-a-service) is a set of infrastructure solutions to ensure smooth running of IT infrastructure. They allow you to move the entire infrastructure or a part of it in a third party cloud environment, in the event of failures in IT systems and other force majeure, for example human errors, fires, floods, power outages.
Planning for disaster recovery is essential for business continuity. The service enables the business to return to its usual operation within the time period specified by a particular solution.
Cloud constructor
Backup Solution
Data backupActive - Passive
from 35,7 $ per month
RTO/RPO: depends on data volume/from 1 hour
All types of business (including small business)
Non-critical data recovery time, small data losses
3+ copies and versions
Multiple recovery points
Geo-distributed storage
Recovering partially damaged and lost data
Learn more
VM Replication Solution
Replication of data to a remote siteActive - Standby
from 110 $ per month
RTO/RPO: from 30 minutes/from 15 minutes
web-platforms, e-commerce, BigData
Disaster Recovery, Business Continuity
SLA 99.982%
Multiple replica recovery points
Simplified failover and failback
Near-CDP for any virtualized application
Learn more
SyncCluster
Synchronous data mirroringActive - Active
from 229 $ per month
RTO/RPO: from 30 seconds/ 0 seconds
Banks, large IT and government agencies, BigData
High disaster tolerance and service availability
SLA 99.99%
Protection from natural disasters
Distance between data centers 10 km
Replication is provided at the Data Storage System
Learn more
Benefits of cloud disaster recovery
- No CAPEX
- Easy deployment and testing
- Opportunity to build multi-cloud solutions
- Two Tier III data centers
- High expertise
- DRP (disaster recovery plan)
Why trust Cloud4U
FAQ
What is Backup Data Center?
A Backup Data Center is a secondary facility designed to store and protect an organization's critical data and IT infrastructure. It serves as a contingency site that can be activated in the event of a primary data center failure due to disasters, cyberattacks, or other disruptions.Key features include:
- Data Redundancy: Regular backups of data from the primary data center are stored to ensure data integrity and availability.
- Disaster Recovery: The backup data center is equipped with the necessary hardware and software to quickly restore operations and minimize downtime.
- Geographic Separation: Typically located in a different geographic area than the primary data center to mitigate risks associated with localized events.
- Testing and Maintenance: Regular testing of backup systems and recovery processes ensures readiness for rapid activation when needed.
Overall, a Backup Data Center is essential for achieving business continuity and resilience in the face of unforeseen incidents.
Can I customize my DRaaS solution to fit my business needs?
Is my data secure in a DRaaS environment?
Yes, your data can be secure in a DRaaS environment, provided you choose a reputable provider that implements robust security measures. Key security features to look for include:
- Data Encryption: All data should be encrypted both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Access Controls: Strong access management protocols ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
- Compliance Standards: The provider should adhere to industry-specific compliance regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) to ensure data protection and privacy.
- Regular Security Audits: Providers should conduct regular security assessments and audits to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities.
- Isolation of Accounts: Customer accounts should be isolated to prevent any cross-access between different users' data.
By evaluating these security aspects, you can ensure that your data remains protected within a DRaaS solution
How often should I test my DRaaS plan?
It is recommended to test your Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) plan at least once a year to ensure its effectiveness and readiness for potential disasters. However, the frequency may vary based on several factors, such as:
- Significant changes in your IT infrastructure or business operations.
- Regulatory requirements that mandate more frequent testing.
- The complexity and size of your IT environment, which may necessitate more regular evaluations.
For organizations operating in high-risk environments or those that have experienced recent incidents, testing may need to occur more frequently, potentially several times a year. Regular testing helps identify gaps in the plan and ensures that recovery objectives are achievable when needed.
What are Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTO)?
Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) are critical metrics in disaster recovery planning.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) defines the maximum acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. It indicates how old the data can be at the time of recovery, essentially determining the frequency of backups needed to minimize data loss. For example, an RPO of one hour means that data should be backed up at least every hour to ensure no more than one hour's worth of data is lost during a disruption.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO) specifies the maximum acceptable downtime after a disaster occurs. It measures how quickly systems and applications must be restored to resume normal operations. For instance, an RTO of four hours means that services should be back online within four hours after a failure.
Together, RPO and RTO help organizations establish their disaster recovery strategies, balancing data loss tolerance and downtime expectations.
Are there any additional costs associated with data recovery?
Can I backup the entire VM or is it possible to backup specific files and folders?
What types of disasters does DRaaS protect against?
DRaaS protects against various types of disasters, including:
- Natural Disasters: Events such as earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and fires that can damage physical infrastructure.
- Cyberattacks: Threats like ransomware, malware, and hacking attempts that compromise data integrity and availability.
- Hardware Failures: Malfunctions in physical servers or storage devices that can lead to data loss or downtime.
- Human Errors: Mistakes made by employees, such as accidental deletions or misconfigurations, which can disrupt operations.
- Power Outages: Interruptions in power supply that affect data center operations and access to critical systems.
By leveraging DRaaS, organizations can ensure business continuity and minimize downtime in the face of these potential threats.
What is DRaaS and how does it work?
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) is a cloud-based solution that enables organizations to back up their IT infrastructure and data in a third-party cloud environment. In the event of a disaster—such as a cyberattack, hardware failure, or natural disaster—DRaaS allows for rapid recovery of applications and data to minimize downtime.How it works:
- Data Replication: Critical data and applications are continuously replicated to the cloud, ensuring up-to-date backups.
- Failover Process: In case of a disaster, the failover process is initiated, redirecting traffic to the cloud-based backup environment.
- Recovery: Once the primary infrastructure is restored, operations can be switched back from the cloud to the on-premises environment, ensuring business continuity.
DRaaS provides organizations with a scalable and cost-effective approach to disaster recovery without the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure.
How quickly can I recover my data with DRaaS?
Are there any additional costs associated with data recovery?
How do I choose the right DRaaS provider?
To choose the right Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) provider, consider the following key factors:
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Evaluate the provider's SLAs to ensure they align with your organization's Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO). Look for clear commitments regarding recovery times and data availability.
- Data Security and Compliance: Assess the provider's security measures, including encryption protocols and compliance with relevant regulations, to ensure your data is protected against breaches and legal issues.
- Scalability: Ensure the DRaaS solution can scale with your business needs, accommodating growth in data volume and application complexity without compromising performance.
- Transparent Pricing: Look for a clear pricing structure that outlines all costs, including potential fees for data recovery or additional services, to avoid unexpected expenses.
- Support and Expertise: Choose a provider that offers ongoing support and has a strong reputation in the industry. Review client testimonials and case studies to gauge their reliability and service quality.
By carefully evaluating these criteria, you can select a DRaaS provider that meets your organization's specific disaster recovery needs.
