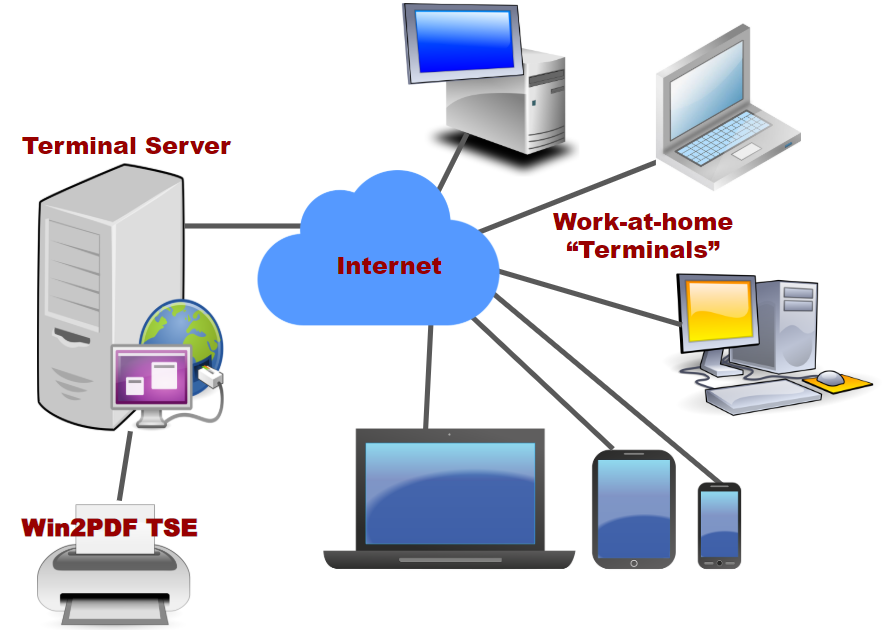
In simple terms, a terminal server is a powerful computer with a server operating system and so-called thin clients connected to it. There are special tools on the server to create sessions for each remote user, running within their sessions the applications they need.
The server contains a number of specialized programs enabling to set up sessions for each remotely connected user. Within these sessions, users can run the desired applications as if they are working on a local PC. In fact, users see only "images" on the screen, transmitted by the server. A mouse and keyboard connected to thin clients are used to work with the computer. Data from them are read and transmitted to the terminal server. As a result, there is an illusion that the programs are running on the client's computers.
Why Use Terminal Server?
The main task of the terminal server is to provide remote service to users. In addition, terminal servers allow the following:
-
Create a centralized infrastructure with a high level of security through the control of remote users and over their access rights.
-
Reduce the cost of the computer park. Maintaining and administering the terminal servers and thin clients is easier and more convenient than expensive PCs.
-
Terminal server can expand and upgrade depending on the number of employees and the complexity of their tasks. It is much easier to maintain one expensive and powerful machine than to buy a large number of computers and components.
-
Work with resource-intensive applications. The terminal server differs from a standard PC in its power and scalability. You can run applications demanding hardware requirements, and these applications are available to all users via thin clients.
In addition, terminal servers help minimize the risks of system failures. The server becomes the only point of failure in the infrastructure, and it can be complemented by power supplies and UPS, failover clusters, geo-distribution systems, etc.
Terminal Server Architecture
Traditionally it consists of three parts:
- A client application for each computer in the network, allowing it to connect to the server through the RDP protocol.
- The RDP protocol. It enables remote work with the desktop of other devices and controls the data exchange between the client and the server.
- A multi-core server is provided for data hosting.
Thick client (fat client)
A thick client is a type of software that executes all user commands regardless of which server is the master. It can be used as an information repository, a program for processing and providing data. The thick client is usually a personal computer or workstation. They have full-fledged software installed to perform the user's tasks.
Thin client
A thin client does not directly perform tasks. Instead, it transfers processing tasks to the server without using its own power to compute and implement the data. It has limited computing power, but enough to start network software such as web interfaces. The use of terminal operation mode is a characteristic feature of thin clients.
Terminal server vs. VDI
Virtual desktops and terminal server have a lot in common. Both technologies are suitable for organizing remote work. Both help to save money on workplace equipment, ensure information security, eliminate the need to buy software for each employee, etc. Which one to implement in a company?
When working with the terminal server all end-users use the same operating system under their personal accounts. Separate sessions are created to isolate users, in which the necessary applications from among those installed on the server are launched. Users have no administrator rights and cannot change the configuration of the operating system. Any failure affects all users.
VDI works differently. Each client has a virtual machine created on the server. It has an independent operating system installed and, in turn, the applications are installed there. An employee working on a virtual machine has much more independence, he can change the OS settings at his discretion, remove applications and install new ones. Failures occurring in virtual machines of neighboring users do not affect the work of others. This is an important advantage of virtualization, but this technology requires powerful and expensive server hardware.
The choice of technology depends on the scale of the IT infrastructure. A terminal server is sufficient in small and medium-sized companies, while in large corporations it is recommended to implement virtualization.